FIPA Compliant Agents
Basic structure of the multi-agent system compliant to FIPA is shown in figure below. An agent is a fundamental actor on an agent platform. Agent platform (AP) provides the physical infrastructure in which agents can be deployed. The AP consists of the machine(s), operating system(s), agent support software, FIPA agent management components and agents. The FIPA agent management components are as follows.
- Agent Management System (AMS) controls access and use of the agent platform and provides services like maintaining a directory of agent names. It provides white page services to other agents. Each agent must be registered with an AMS.
- Message Transport Service (MTS) supports the transportation of FIPA ACL messages between agents on any given AP and between agents on different APs.
- Directory Facilitator (DF) is optional and provides yellow pages services to other agents. Agents may register their services with the DF or query the DF to find out what services are offered by other agents, including the discovery of agents and their offered services in ad hoc networks.
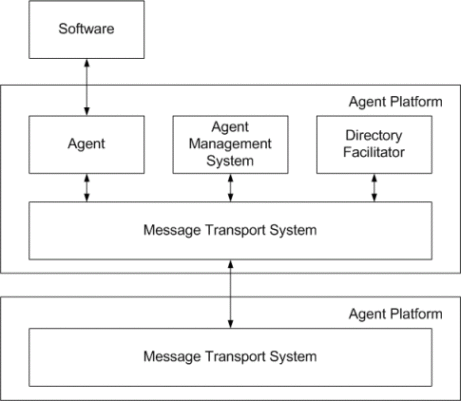
FIPA Agent Management Reference Model
For communication between agents the FIPA Agent Communication Language (ACL) is standardized that is similar to KQML (Knowledge Query and Manipulation Language). An example message in this language follows.
(inform
:sender agent1
:receiver hpl-auction-server
:content (price (bid good02) 150)
:in-reply-to round-4
:reply-with bid04
:language sl
:ontology hpl-auction
)
The ACL message contains several parameters. The only mandatory parameter is
performative (communicative act - such as inform in the previous
example), but most ACL messages will also contain sender,
receiver and content parameters. As we can see, the
ACL message is content independent. The usual language used for expressing
content is a LISP-like Semantic Language SL that is based on KIF. This language allows
expressing propositions and actions. Also, we can see that the content of the
message is ontology independent.
The ontology for the content can be specified
explicitly in a message parameter.
There are several implementations of the core FIPA standards available. Probably the most popular framework is the Java Agent DEvelopment Framework (Jade).
(c) Marek Obitko, 2007 - Terms of use
